- java.lang.Object
-
- java.lang.String
-
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- Serializable, CharSequence, Comparable<String>
public final class String extends Object implements Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence
TheStringclass represents character strings. All string literals in Java programs, such as"abc", are implemented as instances of this class.Strings are constant; their values cannot be changed after they are created. String buffers support mutable strings. Because String objects are immutable they can be shared. For example:
String str = "abc";is equivalent to:
char data[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'}; String str = new String(data);Here are some more examples of how strings can be used:
System.out.println("abc"); String cde = "cde"; System.out.println("abc" + cde); String c = "abc".substring(2,3); String d = cde.substring(1, 2);The class
Stringincludes methods for examining individual characters of the sequence, for comparing strings, for searching strings, for extracting substrings, and for creating a copy of a string with all characters translated to uppercase or to lowercase. Case mapping is based on the Unicode Standard version specified by theCharacterclass.The Java language provides special support for the string concatenation operator ( + ), and for conversion of other objects to strings. String concatenation is implemented through the
StringBuilder(orStringBuffer) class and itsappendmethod. String conversions are implemented through the methodtoString, defined byObjectand inherited by all classes in Java. For additional information on string concatenation and conversion, see Gosling, Joy, and Steele, The Java Language Specification.Unless otherwise noted, passing a
nullargument to a constructor or method in this class will cause aNullPointerExceptionto be thrown.A
Stringrepresents a string in the UTF-16 format in which supplementary characters are represented by surrogate pairs (see the section Unicode Character Representations in theCharacterclass for more information). Index values refer tocharcode units, so a supplementary character uses two positions in aString.The
Stringclass provides methods for dealing with Unicode code points (i.e., characters), in addition to those for dealing with Unicode code units (i.e.,charvalues).Unless otherwise noted, methods for comparing Strings do not take locale into account. The
Collatorclass provides methods for finer-grain, locale-sensitive String comparison.- Since:
- 1.0
- See Also:
Object.toString(),StringBuffer,StringBuilder,Charset, Serialized Form
-
-
Field Summary
Fields Modifier and Type Field and Description static Comparator<String>CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDERA Comparator that ordersStringobjects as bycompareToIgnoreCase.
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description String()Initializes a newly createdStringobject so that it represents an empty character sequence.String(byte[] bytes)Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified array of bytes using the platform's default charset.String(byte[] bytes, Charset charset)Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified array of bytes using the specified charset.String(byte[] ascii, int hibyte)Deprecated.This method does not properly convert bytes into characters. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via theStringconstructors that take aCharset, charset name, or that use the platform's default charset.String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified subarray of bytes using the platform's default charset.String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length, Charset charset)Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified subarray of bytes using the specified charset.String(byte[] ascii, int hibyte, int offset, int count)Deprecated.This method does not properly convert bytes into characters. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via theStringconstructors that take aCharset, charset name, or that use the platform's default charset.String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length, String charsetName)Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified subarray of bytes using the specified charset.String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName)Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified array of bytes using the specified charset.String(char[] value)Allocates a newStringso that it represents the sequence of characters currently contained in the character array argument.String(char[] value, int offset, int count)Allocates a newStringthat contains characters from a subarray of the character array argument.String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count)Allocates a newStringthat contains characters from a subarray of the Unicode code point array argument.String(String original)Initializes a newly createdStringobject so that it represents the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other words, the newly created string is a copy of the argument string.String(StringBuffer buffer)Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters currently contained in the string buffer argument.String(StringBuilder builder)Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters currently contained in the string builder argument.
-
Method Summary
All Methods Static Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Deprecated Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description charcharAt(int index)Returns thecharvalue at the specified index.IntStreamchars()Returns a stream ofintzero-extending thecharvalues from this sequence.intcodePointAt(int index)Returns the character (Unicode code point) at the specified index.intcodePointBefore(int index)Returns the character (Unicode code point) before the specified index.intcodePointCount(int beginIndex, int endIndex)Returns the number of Unicode code points in the specified text range of thisString.IntStreamcodePoints()Returns a stream of code point values from this sequence.intcompareTo(String anotherString)Compares two strings lexicographically.intcompareToIgnoreCase(String str)Compares two strings lexicographically, ignoring case differences.Stringconcat(String str)Concatenates the specified string to the end of this string.booleancontains(CharSequence s)Returns true if and only if this string contains the specified sequence of char values.booleancontentEquals(CharSequence cs)Compares this string to the specifiedCharSequence.booleancontentEquals(StringBuffer sb)Compares this string to the specifiedStringBuffer.static StringcopyValueOf(char[] data)Equivalent tovalueOf(char[]).static StringcopyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count)Equivalent tovalueOf(char[], int, int).booleanendsWith(String suffix)Tests if this string ends with the specified suffix.booleanequals(Object anObject)Compares this string to the specified object.booleanequalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)Compares thisStringto anotherString, ignoring case considerations.static Stringformat(Locale l, String format, Object... args)Returns a formatted string using the specified locale, format string, and arguments.static Stringformat(String format, Object... args)Returns a formatted string using the specified format string and arguments.byte[]getBytes()Encodes thisStringinto a sequence of bytes using the platform's default charset, storing the result into a new byte array.byte[]getBytes(Charset charset)Encodes thisStringinto a sequence of bytes using the given charset, storing the result into a new byte array.voidgetBytes(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, byte[] dst, int dstBegin)Deprecated.This method does not properly convert characters into bytes. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via thegetBytes()method, which uses the platform's default charset.byte[]getBytes(String charsetName)Encodes thisStringinto a sequence of bytes using the named charset, storing the result into a new byte array.voidgetChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)Copies characters from this string into the destination character array.inthashCode()Returns a hash code for this string.intindexOf(int ch)Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character.intindexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character, starting the search at the specified index.intindexOf(String str)Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring.intindexOf(String str, int fromIndex)Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring, starting at the specified index.Stringintern()Returns a canonical representation for the string object.booleanisEmpty()static Stringjoin(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements)Returns a new String composed of copies of theCharSequence elementsjoined together with a copy of the specifieddelimiter.static Stringjoin(CharSequence delimiter, Iterable<? extends CharSequence> elements)Returns a newStringcomposed of copies of theCharSequence elementsjoined together with a copy of the specifieddelimiter.intlastIndexOf(int ch)Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified character.intlastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified character, searching backward starting at the specified index.intlastIndexOf(String str)Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified substring.intlastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified substring, searching backward starting at the specified index.intlength()Returns the length of this string.booleanmatches(String regex)Tells whether or not this string matches the given regular expression.intoffsetByCodePoints(int index, int codePointOffset)Returns the index within thisStringthat is offset from the givenindexbycodePointOffsetcode points.booleanregionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len)Tests if two string regions are equal.booleanregionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len)Tests if two string regions are equal.Stringreplace(char oldChar, char newChar)Returns a string resulting from replacing all occurrences ofoldCharin this string withnewChar.Stringreplace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement)Replaces each substring of this string that matches the literal target sequence with the specified literal replacement sequence.StringreplaceAll(String regex, String replacement)Replaces each substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the given replacement.StringreplaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)Replaces the first substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the given replacement.String[]split(String regex)Splits this string around matches of the given regular expression.String[]split(String regex, int limit)Splits this string around matches of the given regular expression.booleanstartsWith(String prefix)Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix.booleanstartsWith(String prefix, int toffset)Tests if the substring of this string beginning at the specified index starts with the specified prefix.CharSequencesubSequence(int beginIndex, int endIndex)Returns a character sequence that is a subsequence of this sequence.Stringsubstring(int beginIndex)Returns a string that is a substring of this string.Stringsubstring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)Returns a string that is a substring of this string.char[]toCharArray()Converts this string to a new character array.StringtoLowerCase()Converts all of the characters in thisStringto lower case using the rules of the default locale.StringtoLowerCase(Locale locale)Converts all of the characters in thisStringto lower case using the rules of the givenLocale.StringtoString()This object (which is already a string!) is itself returned.StringtoUpperCase()Converts all of the characters in thisStringto upper case using the rules of the default locale.StringtoUpperCase(Locale locale)Converts all of the characters in thisStringto upper case using the rules of the givenLocale.Stringtrim()Returns a string whose value is this string, with any leading and trailing whitespace removed.static StringvalueOf(boolean b)Returns the string representation of thebooleanargument.static StringvalueOf(char c)Returns the string representation of thecharargument.static StringvalueOf(char[] data)Returns the string representation of thechararray argument.static StringvalueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count)Returns the string representation of a specific subarray of thechararray argument.static StringvalueOf(double d)Returns the string representation of thedoubleargument.static StringvalueOf(float f)Returns the string representation of thefloatargument.static StringvalueOf(int i)Returns the string representation of theintargument.static StringvalueOf(long l)Returns the string representation of thelongargument.static StringvalueOf(Object obj)Returns the string representation of theObjectargument.
-
-
-
Field Detail
-
CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
public static final Comparator<String> CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
A Comparator that ordersStringobjects as bycompareToIgnoreCase. This comparator is serializable.Note that this Comparator does not take locale into account, and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales. The
Collatorclass provides locale-sensitive comparison.- Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
Collator
-
-
Constructor Detail
-
String
public String()
Initializes a newly createdStringobject so that it represents an empty character sequence. Note that use of this constructor is unnecessary since Strings are immutable.
-
String
public String(String original)
Initializes a newly createdStringobject so that it represents the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other words, the newly created string is a copy of the argument string. Unless an explicit copy oforiginalis needed, use of this constructor is unnecessary since Strings are immutable.- Parameters:
original- AString
-
String
public String(char[] value)
Allocates a newStringso that it represents the sequence of characters currently contained in the character array argument. The contents of the character array are copied; subsequent modification of the character array does not affect the newly created string.- Parameters:
value- The initial value of the string
-
String
public String(char[] value, int offset, int count)Allocates a newStringthat contains characters from a subarray of the character array argument. Theoffsetargument is the index of the first character of the subarray and thecountargument specifies the length of the subarray. The contents of the subarray are copied; subsequent modification of the character array does not affect the newly created string.- Parameters:
value- Array that is the source of charactersoffset- The initial offsetcount- The length- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- Ifoffsetis negative,countis negative, oroffsetis greater thanvalue.length - count
-
String
public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count)Allocates a newStringthat contains characters from a subarray of the Unicode code point array argument. Theoffsetargument is the index of the first code point of the subarray and thecountargument specifies the length of the subarray. The contents of the subarray are converted tochars; subsequent modification of theintarray does not affect the newly created string.- Parameters:
codePoints- Array that is the source of Unicode code pointsoffset- The initial offsetcount- The length- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- If any invalid Unicode code point is found incodePointsIndexOutOfBoundsException- Ifoffsetis negative,countis negative, oroffsetis greater thancodePoints.length - count- Since:
- 1.5
-
String
@Deprecated public String(byte[] ascii, int hibyte, int offset, int count)
Deprecated. This method does not properly convert bytes into characters. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via theStringconstructors that take aCharset, charset name, or that use the platform's default charset.Allocates a newStringconstructed from a subarray of an array of 8-bit integer values.The
offsetargument is the index of the first byte of the subarray, and thecountargument specifies the length of the subarray.Each
bytein the subarray is converted to acharas specified in the method above.- Parameters:
ascii- The bytes to be converted to charactershibyte- The top 8 bits of each 16-bit Unicode code unitoffset- The initial offsetcount- The length- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- Ifoffsetis negative,countis negative, oroffsetis greater thanascii.length - count- See Also:
String(byte[], int),String(byte[], int, int, java.lang.String),String(byte[], int, int, java.nio.charset.Charset),String(byte[], int, int),String(byte[], java.lang.String),String(byte[], java.nio.charset.Charset),String(byte[])
-
String
@Deprecated public String(byte[] ascii, int hibyte)
Deprecated. This method does not properly convert bytes into characters. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via theStringconstructors that take aCharset, charset name, or that use the platform's default charset.Allocates a newStringcontaining characters constructed from an array of 8-bit integer values. Each character cin the resulting string is constructed from the corresponding component b in the byte array such that:c == (char)(((hibyte & 0xff) << 8) | (b & 0xff))- Parameters:
ascii- The bytes to be converted to charactershibyte- The top 8 bits of each 16-bit Unicode code unit- See Also:
String(byte[], int, int, java.lang.String),String(byte[], int, int, java.nio.charset.Charset),String(byte[], int, int),String(byte[], java.lang.String),String(byte[], java.nio.charset.Charset),String(byte[])
-
String
public String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length, String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingExceptionConstructs a newStringby decoding the specified subarray of bytes using the specified charset. The length of the newStringis a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the length of the subarray.The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid in the given charset is unspecified. The
CharsetDecoderclass should be used when more control over the decoding process is required.- Parameters:
bytes- The bytes to be decoded into charactersoffset- The index of the first byte to decodelength- The number of bytes to decodecharsetName- The name of a supported charset- Throws:
UnsupportedEncodingException- If the named charset is not supportedIndexOutOfBoundsException- Ifoffsetis negative,lengthis negative, oroffsetis greater thanbytes.length - length- Since:
- 1.1
-
String
public String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length, Charset charset)Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified subarray of bytes using the specified charset. The length of the newStringis a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the length of the subarray.This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character sequences with this charset's default replacement string. The
CharsetDecoderclass should be used when more control over the decoding process is required.- Parameters:
bytes- The bytes to be decoded into charactersoffset- The index of the first byte to decodelength- The number of bytes to decodecharset- The charset to be used to decode thebytes- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- Ifoffsetis negative,lengthis negative, oroffsetis greater thanbytes.length - length- Since:
- 1.6
-
String
public String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingExceptionConstructs a newStringby decoding the specified array of bytes using the specified charset. The length of the newStringis a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the length of the byte array.The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid in the given charset is unspecified. The
CharsetDecoderclass should be used when more control over the decoding process is required.- Parameters:
bytes- The bytes to be decoded into characterscharsetName- The name of a supported charset- Throws:
UnsupportedEncodingException- If the named charset is not supported- Since:
- 1.1
-
String
public String(byte[] bytes, Charset charset)Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified array of bytes using the specified charset. The length of the newStringis a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the length of the byte array.This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character sequences with this charset's default replacement string. The
CharsetDecoderclass should be used when more control over the decoding process is required.- Parameters:
bytes- The bytes to be decoded into characterscharset- The charset to be used to decode thebytes- Since:
- 1.6
-
String
public String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified subarray of bytes using the platform's default charset. The length of the newStringis a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the length of the subarray.The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid in the default charset is unspecified. The
CharsetDecoderclass should be used when more control over the decoding process is required.- Parameters:
bytes- The bytes to be decoded into charactersoffset- The index of the first byte to decodelength- The number of bytes to decode- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- Ifoffsetis negative,lengthis negative, oroffsetis greater thanbytes.length - length- Since:
- 1.1
-
String
public String(byte[] bytes)
Constructs a newStringby decoding the specified array of bytes using the platform's default charset. The length of the newStringis a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the length of the byte array.The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid in the default charset is unspecified. The
CharsetDecoderclass should be used when more control over the decoding process is required.- Parameters:
bytes- The bytes to be decoded into characters- Since:
- 1.1
-
String
public String(StringBuffer buffer)
Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters currently contained in the string buffer argument. The contents of the string buffer are copied; subsequent modification of the string buffer does not affect the newly created string.- Parameters:
buffer- AStringBuffer
-
String
public String(StringBuilder builder)
Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters currently contained in the string builder argument. The contents of the string builder are copied; subsequent modification of the string builder does not affect the newly created string.This constructor is provided to ease migration to
StringBuilder. Obtaining a string from a string builder via thetoStringmethod is likely to run faster and is generally preferred.- Parameters:
builder- AStringBuilder- Since:
- 1.5
-
-
Method Detail
-
length
public int length()
Returns the length of this string. The length is equal to the number of Unicode code units in the string.- Specified by:
lengthin interfaceCharSequence- Returns:
- the length of the sequence of characters represented by this object.
-
isEmpty
public boolean isEmpty()
- Returns:
trueiflength()is0, otherwisefalse- Since:
- 1.6
-
charAt
public char charAt(int index)
Returns thecharvalue at the specified index. An index ranges from0tolength() - 1. The firstcharvalue of the sequence is at index0, the next at index1, and so on, as for array indexing.If the
charvalue specified by the index is a surrogate, the surrogate value is returned.- Specified by:
charAtin interfaceCharSequence- Parameters:
index- the index of thecharvalue.- Returns:
- the
charvalue at the specified index of this string. The firstcharvalue is at index0. - Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- if theindexargument is negative or not less than the length of this string.
-
codePointAt
public int codePointAt(int index)
Returns the character (Unicode code point) at the specified index. The index refers tocharvalues (Unicode code units) and ranges from0tolength()- 1.If the
charvalue specified at the given index is in the high-surrogate range, the following index is less than the length of thisString, and thecharvalue at the following index is in the low-surrogate range, then the supplementary code point corresponding to this surrogate pair is returned. Otherwise, thecharvalue at the given index is returned.- Parameters:
index- the index to thecharvalues- Returns:
- the code point value of the character at the
index - Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- if theindexargument is negative or not less than the length of this string.- Since:
- 1.5
-
codePointBefore
public int codePointBefore(int index)
Returns the character (Unicode code point) before the specified index. The index refers tocharvalues (Unicode code units) and ranges from1tolength.If the
charvalue at(index - 1)is in the low-surrogate range,(index - 2)is not negative, and thecharvalue at(index - 2)is in the high-surrogate range, then the supplementary code point value of the surrogate pair is returned. If thecharvalue atindex - 1is an unpaired low-surrogate or a high-surrogate, the surrogate value is returned.- Parameters:
index- the index following the code point that should be returned- Returns:
- the Unicode code point value before the given index.
- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- if theindexargument is less than 1 or greater than the length of this string.- Since:
- 1.5
-
codePointCount
public int codePointCount(int beginIndex, int endIndex)Returns the number of Unicode code points in the specified text range of thisString. The text range begins at the specifiedbeginIndexand extends to thecharat indexendIndex - 1. Thus the length (inchars) of the text range isendIndex-beginIndex. Unpaired surrogates within the text range count as one code point each.- Parameters:
beginIndex- the index to the firstcharof the text range.endIndex- the index after the lastcharof the text range.- Returns:
- the number of Unicode code points in the specified text range
- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- if thebeginIndexis negative, orendIndexis larger than the length of thisString, orbeginIndexis larger thanendIndex.- Since:
- 1.5
-
offsetByCodePoints
public int offsetByCodePoints(int index, int codePointOffset)Returns the index within thisStringthat is offset from the givenindexbycodePointOffsetcode points. Unpaired surrogates within the text range given byindexandcodePointOffsetcount as one code point each.- Parameters:
index- the index to be offsetcodePointOffset- the offset in code points- Returns:
- the index within this
String - Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifindexis negative or larger then the length of thisString, or ifcodePointOffsetis positive and the substring starting withindexhas fewer thancodePointOffsetcode points, or ifcodePointOffsetis negative and the substring beforeindexhas fewer than the absolute value ofcodePointOffsetcode points.- Since:
- 1.5
-
getChars
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)Copies characters from this string into the destination character array.The first character to be copied is at index
srcBegin; the last character to be copied is at indexsrcEnd-1(thus the total number of characters to be copied issrcEnd-srcBegin). The characters are copied into the subarray ofdststarting at indexdstBeginand ending at index:dstBegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1- Parameters:
srcBegin- index of the first character in the string to copy.srcEnd- index after the last character in the string to copy.dst- the destination array.dstBegin- the start offset in the destination array.- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- If any of the following is true:srcBeginis negative.srcBeginis greater thansrcEndsrcEndis greater than the length of this stringdstBeginis negativedstBegin+(srcEnd-srcBegin)is larger thandst.length
-
getBytes
@Deprecated public void getBytes(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, byte[] dst, int dstBegin)
Deprecated. This method does not properly convert characters into bytes. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via thegetBytes()method, which uses the platform's default charset.Copies characters from this string into the destination byte array. Each byte receives the 8 low-order bits of the corresponding character. The eight high-order bits of each character are not copied and do not participate in the transfer in any way.The first character to be copied is at index
srcBegin; the last character to be copied is at indexsrcEnd-1. The total number of characters to be copied issrcEnd-srcBegin. The characters, converted to bytes, are copied into the subarray ofdststarting at indexdstBeginand ending at index:dstBegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1- Parameters:
srcBegin- Index of the first character in the string to copysrcEnd- Index after the last character in the string to copydst- The destination arraydstBegin- The start offset in the destination array- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- If any of the following is true:-
srcBeginis negative -
srcBeginis greater thansrcEnd -
srcEndis greater than the length of this String -
dstBeginis negative -
dstBegin+(srcEnd-srcBegin)is larger thandst.length
-
-
getBytes
public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException
Encodes thisStringinto a sequence of bytes using the named charset, storing the result into a new byte array.The behavior of this method when this string cannot be encoded in the given charset is unspecified. The
CharsetEncoderclass should be used when more control over the encoding process is required.- Parameters:
charsetName- The name of a supported charset- Returns:
- The resultant byte array
- Throws:
UnsupportedEncodingException- If the named charset is not supported- Since:
- 1.1
-
getBytes
public byte[] getBytes(Charset charset)
Encodes thisStringinto a sequence of bytes using the given charset, storing the result into a new byte array.This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character sequences with this charset's default replacement byte array. The
CharsetEncoderclass should be used when more control over the encoding process is required.- Parameters:
charset- The Charset to be used to encode theString- Returns:
- The resultant byte array
- Since:
- 1.6
-
getBytes
public byte[] getBytes()
Encodes thisStringinto a sequence of bytes using the platform's default charset, storing the result into a new byte array.The behavior of this method when this string cannot be encoded in the default charset is unspecified. The
CharsetEncoderclass should be used when more control over the encoding process is required.- Returns:
- The resultant byte array
- Since:
- 1.1
-
equals
public boolean equals(Object anObject)
Compares this string to the specified object. The result istrueif and only if the argument is notnulland is aStringobject that represents the same sequence of characters as this object.For finer-grained String comparison, refer to
Collator.- Overrides:
equalsin classObject- Parameters:
anObject- The object to compare thisStringagainst- Returns:
trueif the given object represents aStringequivalent to this string,falseotherwise- See Also:
compareTo(String),equalsIgnoreCase(String)
-
contentEquals
public boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb)
Compares this string to the specifiedStringBuffer. The result istrueif and only if thisStringrepresents the same sequence of characters as the specifiedStringBuffer. This method synchronizes on theStringBuffer.For finer-grained String comparison, refer to
Collator.- Parameters:
sb- TheStringBufferto compare thisStringagainst- Returns:
trueif thisStringrepresents the same sequence of characters as the specifiedStringBuffer,falseotherwise- Since:
- 1.4
-
contentEquals
public boolean contentEquals(CharSequence cs)
Compares this string to the specifiedCharSequence. The result istrueif and only if thisStringrepresents the same sequence of char values as the specified sequence. Note that if theCharSequenceis aStringBufferthen the method synchronizes on it.For finer-grained String comparison, refer to
Collator.- Parameters:
cs- The sequence to compare thisStringagainst- Returns:
trueif thisStringrepresents the same sequence of char values as the specified sequence,falseotherwise- Since:
- 1.5
-
equalsIgnoreCase
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
Compares thisStringto anotherString, ignoring case considerations. Two strings are considered equal ignoring case if they are of the same length and corresponding characters in the two strings are equal ignoring case.Two characters
c1andc2are considered the same ignoring case if at least one of the following is true:- The two characters are the same (as compared by the
==operator) - Calling
Character.toLowerCase(Character.toUpperCase(char))on each character produces the same result
Note that this method does not take locale into account, and will result in unsatisfactory results for certain locales. The
Collatorclass provides locale-sensitive comparison.- Parameters:
anotherString- TheStringto compare thisStringagainst- Returns:
trueif the argument is notnulland it represents an equivalentStringignoring case;falseotherwise- See Also:
equals(Object)
- The two characters are the same (as compared by the
-
compareTo
public int compareTo(String anotherString)
Compares two strings lexicographically. The comparison is based on the Unicode value of each character in the strings. The character sequence represented by thisStringobject is compared lexicographically to the character sequence represented by the argument string. The result is a negative integer if thisStringobject lexicographically precedes the argument string. The result is a positive integer if thisStringobject lexicographically follows the argument string. The result is zero if the strings are equal;compareToreturns0exactly when theequals(Object)method would returntrue.This is the definition of lexicographic ordering. If two strings are different, then either they have different characters at some index that is a valid index for both strings, or their lengths are different, or both. If they have different characters at one or more index positions, let k be the smallest such index; then the string whose character at position k has the smaller value, as determined by using the
<operator, lexicographically precedes the other string. In this case,compareToreturns the difference of the two character values at positionkin the two string -- that is, the value:
If there is no index position at which they differ, then the shorter string lexicographically precedes the longer string. In this case,this.charAt(k)-anotherString.charAt(k)
compareToreturns the difference of the lengths of the strings -- that is, the value:this.length()-anotherString.length()
For finer-grained String comparison, refer to
Collator.- Specified by:
compareToin interfaceComparable<String>- Parameters:
anotherString- theStringto be compared.- Returns:
- the value
0if the argument string is equal to this string; a value less than0if this string is lexicographically less than the string argument; and a value greater than0if this string is lexicographically greater than the string argument.
-
compareToIgnoreCase
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
Compares two strings lexicographically, ignoring case differences. This method returns an integer whose sign is that of callingcompareTowith normalized versions of the strings where case differences have been eliminated by callingCharacter.toLowerCase(Character.toUpperCase(character))on each character.Note that this method does not take locale into account, and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales. The
Collatorclass provides locale-sensitive comparison.- Parameters:
str- theStringto be compared.- Returns:
- a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the specified String is greater than, equal to, or less than this String, ignoring case considerations.
- Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
Collator
-
regionMatches
public boolean regionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len)Tests if two string regions are equal.A substring of this
Stringobject is compared to a substring of the argument other. The result is true if these substrings represent identical character sequences. The substring of thisStringobject to be compared begins at indextoffsetand has lengthlen. The substring of other to be compared begins at indexooffsetand has lengthlen. The result isfalseif and only if at least one of the following is true:toffsetis negative.ooffsetis negative.toffset+lenis greater than the length of thisStringobject.ooffset+lenis greater than the length of the other argument.- There is some nonnegative integer k less than
lensuch that:this.charAt(toffset +k) != other.charAt(ooffset +k)
Note that this method does not take locale into account. The
Collatorclass provides locale-sensitive comparison.- Parameters:
toffset- the starting offset of the subregion in this string.other- the string argument.ooffset- the starting offset of the subregion in the string argument.len- the number of characters to compare.- Returns:
trueif the specified subregion of this string exactly matches the specified subregion of the string argument;falseotherwise.
-
regionMatches
public boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len)Tests if two string regions are equal.A substring of this
Stringobject is compared to a substring of the argumentother. The result istrueif these substrings represent character sequences that are the same, ignoring case if and only ifignoreCaseis true. The substring of thisStringobject to be compared begins at indextoffsetand has lengthlen. The substring ofotherto be compared begins at indexooffsetand has lengthlen. The result isfalseif and only if at least one of the following is true:toffsetis negative.ooffsetis negative.toffset+lenis greater than the length of thisStringobject.ooffset+lenis greater than the length of the other argument.ignoreCaseisfalseand there is some nonnegative integer k less thanlensuch that:this.charAt(toffset+k) != other.charAt(ooffset+k)
ignoreCaseistrueand there is some nonnegative integer k less thanlensuch that:Character.toLowerCase(Character.toUpperCase(this.charAt(toffset+k))) != Character.toLowerCase(Character.toUpperCase(other.charAt(ooffset+k)))
Note that this method does not take locale into account, and will result in unsatisfactory results for certain locales when
ignoreCaseistrue. TheCollatorclass provides locale-sensitive comparison.- Parameters:
ignoreCase- iftrue, ignore case when comparing characters.toffset- the starting offset of the subregion in this string.other- the string argument.ooffset- the starting offset of the subregion in the string argument.len- the number of characters to compare.- Returns:
trueif the specified subregion of this string matches the specified subregion of the string argument;falseotherwise. Whether the matching is exact or case insensitive depends on theignoreCaseargument.
-
startsWith
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset)
Tests if the substring of this string beginning at the specified index starts with the specified prefix.- Parameters:
prefix- the prefix.toffset- where to begin looking in this string.- Returns:
trueif the character sequence represented by the argument is a prefix of the substring of this object starting at indextoffset;falseotherwise. The result isfalseiftoffsetis negative or greater than the length of thisStringobject; otherwise the result is the same as the result of the expressionthis.substring(toffset).startsWith(prefix)
-
startsWith
public boolean startsWith(String prefix)
Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix.- Parameters:
prefix- the prefix.- Returns:
trueif the character sequence represented by the argument is a prefix of the character sequence represented by this string;falseotherwise. Note also thattruewill be returned if the argument is an empty string or is equal to thisStringobject as determined by theequals(Object)method.- Since:
- 1.0
-
endsWith
public boolean endsWith(String suffix)
Tests if this string ends with the specified suffix.- Parameters:
suffix- the suffix.- Returns:
trueif the character sequence represented by the argument is a suffix of the character sequence represented by this object;falseotherwise. Note that the result will betrueif the argument is the empty string or is equal to thisStringobject as determined by theequals(Object)method.
-
hashCode
public int hashCode()
Returns a hash code for this string. The hash code for aStringobject is computed as
usings[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1]
intarithmetic, wheres[i]is the ith character of the string,nis the length of the string, and^indicates exponentiation. (The hash value of the empty string is zero.)- Overrides:
hashCodein classObject- Returns:
- a hash code value for this object.
- See Also:
Object.equals(java.lang.Object),System.identityHashCode(java.lang.Object)
-
indexOf
public int indexOf(int ch)
Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character. If a character with valuechoccurs in the character sequence represented by thisStringobject, then the index (in Unicode code units) of the first such occurrence is returned. For values ofchin the range from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive), this is the smallest value k such that:
is true. For other values ofthis.charAt(k) == ch
ch, it is the smallest value k such that:
is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this string, thenthis.codePointAt(k) == ch
-1is returned.- Parameters:
ch- a character (Unicode code point).- Returns:
- the index of the first occurrence of the character in the
character sequence represented by this object, or
-1if the character does not occur.
-
indexOf
public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character, starting the search at the specified index.If a character with value
choccurs in the character sequence represented by thisStringobject at an index no smaller thanfromIndex, then the index of the first such occurrence is returned. For values ofchin the range from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive), this is the smallest value k such that:
is true. For other values of(this.charAt(k) == ch)
&&(k >= fromIndex)ch, it is the smallest value k such that:
is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this string at or after position(this.codePointAt(k) == ch)
&&(k >= fromIndex)fromIndex, then-1is returned.There is no restriction on the value of
fromIndex. If it is negative, it has the same effect as if it were zero: this entire string may be searched. If it is greater than the length of this string, it has the same effect as if it were equal to the length of this string:-1is returned.All indices are specified in
charvalues (Unicode code units).- Parameters:
ch- a character (Unicode code point).fromIndex- the index to start the search from.- Returns:
- the index of the first occurrence of the character in the
character sequence represented by this object that is greater
than or equal to
fromIndex, or-1if the character does not occur.
-
lastIndexOf
public int lastIndexOf(int ch)
Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified character. For values ofchin the range from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive), the index (in Unicode code units) returned is the largest value k such that:
is true. For other values ofthis.charAt(k) == ch
ch, it is the largest value k such that:
is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this string, thenthis.codePointAt(k) == ch
-1is returned. TheStringis searched backwards starting at the last character.- Parameters:
ch- a character (Unicode code point).- Returns:
- the index of the last occurrence of the character in the
character sequence represented by this object, or
-1if the character does not occur.
-
lastIndexOf
public int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified character, searching backward starting at the specified index. For values ofchin the range from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive), the index returned is the largest value k such that:
is true. For other values of(this.charAt(k) == ch)
&&(k <= fromIndex)ch, it is the largest value k such that:
is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this string at or before position(this.codePointAt(k) == ch)
&&(k <= fromIndex)fromIndex, then-1is returned.All indices are specified in
charvalues (Unicode code units).- Parameters:
ch- a character (Unicode code point).fromIndex- the index to start the search from. There is no restriction on the value offromIndex. If it is greater than or equal to the length of this string, it has the same effect as if it were equal to one less than the length of this string: this entire string may be searched. If it is negative, it has the same effect as if it were -1: -1 is returned.- Returns:
- the index of the last occurrence of the character in the
character sequence represented by this object that is less
than or equal to
fromIndex, or-1if the character does not occur before that point.
-
indexOf
public int indexOf(String str)
Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring.The returned index is the smallest value
kfor which:
If no such value ofthis.startsWith(str, k)kexists, then-1is returned.- Parameters:
str- the substring to search for.- Returns:
- the index of the first occurrence of the specified substring,
or
-1if there is no such occurrence.
-
indexOf
public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring, starting at the specified index.The returned index is the smallest value
kfor which:
If no such value ofk >= Math.min(fromIndex, this.length()) && this.startsWith(str, k)kexists, then-1is returned.- Parameters:
str- the substring to search for.fromIndex- the index from which to start the search.- Returns:
- the index of the first occurrence of the specified substring,
starting at the specified index,
or
-1if there is no such occurrence.
-
lastIndexOf
public int lastIndexOf(String str)
Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified substring. The last occurrence of the empty string "" is considered to occur at the index valuethis.length().The returned index is the largest value
kfor which:
If no such value ofthis.startsWith(str, k)kexists, then-1is returned.- Parameters:
str- the substring to search for.- Returns:
- the index of the last occurrence of the specified substring,
or
-1if there is no such occurrence.
-
lastIndexOf
public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified substring, searching backward starting at the specified index.The returned index is the largest value
kfor which:
If no such value ofk <= Math.min(fromIndex, this.length()) && this.startsWith(str, k)kexists, then-1is returned.- Parameters:
str- the substring to search for.fromIndex- the index to start the search from.- Returns:
- the index of the last occurrence of the specified substring,
searching backward from the specified index,
or
-1if there is no such occurrence.
-
substring
public String substring(int beginIndex)
Returns a string that is a substring of this string. The substring begins with the character at the specified index and extends to the end of this string.Examples:
"unhappy".substring(2) returns "happy" "Harbison".substring(3) returns "bison" "emptiness".substring(9) returns "" (an empty string)
- Parameters:
beginIndex- the beginning index, inclusive.- Returns:
- the specified substring.
- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifbeginIndexis negative or larger than the length of thisStringobject.
-
substring
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
Returns a string that is a substring of this string. The substring begins at the specifiedbeginIndexand extends to the character at indexendIndex - 1. Thus the length of the substring isendIndex-beginIndex.Examples:
"hamburger".substring(4, 8) returns "urge" "smiles".substring(1, 5) returns "mile"
- Parameters:
beginIndex- the beginning index, inclusive.endIndex- the ending index, exclusive.- Returns:
- the specified substring.
- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- if thebeginIndexis negative, orendIndexis larger than the length of thisStringobject, orbeginIndexis larger thanendIndex.
-
subSequence
public CharSequence subSequence(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
Returns a character sequence that is a subsequence of this sequence.An invocation of this method of the form
behaves in exactly the same way as the invocationstr.subSequence(begin, end)
str.substring(begin, end)
- Specified by:
subSequencein interfaceCharSequence- API Note:
- This method is defined so that the
Stringclass can implement theCharSequenceinterface. - Parameters:
beginIndex- the begin index, inclusive.endIndex- the end index, exclusive.- Returns:
- the specified subsequence.
- Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifbeginIndexorendIndexis negative, ifendIndexis greater thanlength(), or ifbeginIndexis greater thanendIndex- Since:
- 1.4
-
concat
public String concat(String str)
Concatenates the specified string to the end of this string.If the length of the argument string is
0, then thisStringobject is returned. Otherwise, aStringobject is returned that represents a character sequence that is the concatenation of the character sequence represented by thisStringobject and the character sequence represented by the argument string.Examples:
"cares".concat("s") returns "caress" "to".concat("get").concat("her") returns "together"- Parameters:
str- theStringthat is concatenated to the end of thisString.- Returns:
- a string that represents the concatenation of this object's characters followed by the string argument's characters.
-
replace
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
Returns a string resulting from replacing all occurrences ofoldCharin this string withnewChar.If the character
oldChardoes not occur in the character sequence represented by thisStringobject, then a reference to thisStringobject is returned. Otherwise, aStringobject is returned that represents a character sequence identical to the character sequence represented by thisStringobject, except that every occurrence ofoldCharis replaced by an occurrence ofnewChar.Examples:
"mesquite in your cellar".replace('e', 'o') returns "mosquito in your collar" "the war of baronets".replace('r', 'y') returns "the way of bayonets" "sparring with a purple porpoise".replace('p', 't') returns "starring with a turtle tortoise" "JonL".replace('q', 'x') returns "JonL" (no change)- Parameters:
oldChar- the old character.newChar- the new character.- Returns:
- a string derived from this string by replacing every
occurrence of
oldCharwithnewChar.
-
matches
public boolean matches(String regex)
Tells whether or not this string matches the given regular expression.An invocation of this method of the form str
.matches(regex)yields exactly the same result as the expressionPattern.matches(regex, str)- Parameters:
regex- the regular expression to which this string is to be matched- Returns:
trueif, and only if, this string matches the given regular expression- Throws:
PatternSyntaxException- if the regular expression's syntax is invalid- Since:
- 1.4
- See Also:
Pattern
-
contains
public boolean contains(CharSequence s)
Returns true if and only if this string contains the specified sequence of char values.- Parameters:
s- the sequence to search for- Returns:
- true if this string contains
s, false otherwise - Since:
- 1.5
-
replaceFirst
public String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)
Replaces the first substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the given replacement.An invocation of this method of the form str
.replaceFirst(regex,repl)yields exactly the same result as the expressionPattern.compile(regex).matcher(str).replaceFirst(repl)Note that backslashes (
\) and dollar signs ($) in the replacement string may cause the results to be different than if it were being treated as a literal replacement string; seeMatcher.replaceFirst(java.lang.String). UseMatcher.quoteReplacement(java.lang.String)to suppress the special meaning of these characters, if desired.- Parameters:
regex- the regular expression to which this string is to be matchedreplacement- the string to be substituted for the first match- Returns:
- The resulting
String - Throws:
PatternSyntaxException- if the regular expression's syntax is invalid- Since:
- 1.4
- See Also:
Pattern
-
replaceAll
public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement)
Replaces each substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the given replacement.An invocation of this method of the form str
.replaceAll(regex,repl)yields exactly the same result as the expressionPattern.compile(regex).matcher(str).replaceAll(repl)Note that backslashes (
\) and dollar signs ($) in the replacement string may cause the results to be different than if it were being treated as a literal replacement string; seeMatcher.replaceAll. UseMatcher.quoteReplacement(java.lang.String)to suppress the special meaning of these characters, if desired.- Parameters:
regex- the regular expression to which this string is to be matchedreplacement- the string to be substituted for each match- Returns:
- The resulting
String - Throws:
PatternSyntaxException- if the regular expression's syntax is invalid- Since:
- 1.4
- See Also:
Pattern
-
replace
public String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement)
Replaces each substring of this string that matches the literal target sequence with the specified literal replacement sequence. The replacement proceeds from the beginning of the string to the end, for example, replacing "aa" with "b" in the string "aaa" will result in "ba" rather than "ab".- Parameters:
target- The sequence of char values to be replacedreplacement- The replacement sequence of char values- Returns:
- The resulting string
- Since:
- 1.5
-
split
public String[] split(String regex, int limit)
Splits this string around matches of the given regular expression.The array returned by this method contains each substring of this string that is terminated by another substring that matches the given expression or is terminated by the end of the string. The substrings in the array are in the order in which they occur in this string. If the expression does not match any part of the input then the resulting array has just one element, namely this string.
When there is a positive-width match at the beginning of this string then an empty leading substring is included at the beginning of the resulting array. A zero-width match at the beginning however never produces such empty leading substring.
The
limitparameter controls the number of times the pattern is applied and therefore affects the length of the resulting array. If the limit n is greater than zero then the pattern will be applied at most n - 1 times, the array's length will be no greater than n, and the array's last entry will contain all input beyond the last matched delimiter. If n is non-positive then the pattern will be applied as many times as possible and the array can have any length. If n is zero then the pattern will be applied as many times as possible, the array can have any length, and trailing empty strings will be discarded.The string
"boo:and:foo", for example, yields the following results with these parameters:Regex Limit Result : 2 { "boo", "and:foo" }: 5 { "boo", "and", "foo" }: -2 { "boo", "and", "foo" }o 5 { "b", "", ":and:f", "", "" }o -2 { "b", "", ":and:f", "", "" }o 0 { "b", "", ":and:f" }An invocation of this method of the form str.
split(regex,n)yields the same result as the expressionPattern.compile(regex).split(str, n)- Parameters:
regex- the delimiting regular expressionlimit- the result threshold, as described above- Returns:
- the array of strings computed by splitting this string around matches of the given regular expression
- Throws:
PatternSyntaxException- if the regular expression's syntax is invalid- Since:
- 1.4
- See Also:
Pattern
-
split
public String[] split(String regex)
Splits this string around matches of the given regular expression.This method works as if by invoking the two-argument
splitmethod with the given expression and a limit argument of zero. Trailing empty strings are therefore not included in the resulting array.The string
"boo:and:foo", for example, yields the following results with these expressions:Regex Result : { "boo", "and", "foo" }o { "b", "", ":and:f" }- Parameters:
regex- the delimiting regular expression- Returns:
- the array of strings computed by splitting this string around matches of the given regular expression
- Throws:
PatternSyntaxException- if the regular expression's syntax is invalid- Since:
- 1.4
- See Also:
Pattern
-
join
public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements)
Returns a new String composed of copies of theCharSequence elementsjoined together with a copy of the specifieddelimiter.For example,
Note that if an element is null, thenString message = String.join("-", "Java", "is", "cool"); // message returned is: "Java-is-cool""null"is added.- Parameters:
delimiter- the delimiter that separates each elementelements- the elements to join together.- Returns:
- a new
Stringthat is composed of theelementsseparated by thedelimiter - Throws:
NullPointerException- Ifdelimiterorelementsisnull- Since:
- 1.8
- See Also:
StringJoiner
-
join
public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, Iterable<? extends CharSequence> elements)
Returns a newStringcomposed of copies of theCharSequence elementsjoined together with a copy of the specifieddelimiter.For example,
Note that if an individual element isList<String> strings = new LinkedList<>(); strings.add("Java");strings.add("is"); strings.add("cool"); String message = String.join(" ", strings); //message returned is: "Java is cool" Set<String> strings = new LinkedHashSet<>(); strings.add("Java"); strings.add("is"); strings.add("very"); strings.add("cool"); String message = String.join("-", strings); //message returned is: "Java-is-very-cool"null, then"null"is added.- Parameters:
delimiter- a sequence of characters that is used to separate each of theelementsin the resultingStringelements- anIterablethat will have itselementsjoined together.- Returns:
- a new
Stringthat is composed from theelementsargument - Throws:
NullPointerException- Ifdelimiterorelementsisnull- Since:
- 1.8
- See Also:
join(CharSequence,CharSequence...),StringJoiner
-
toLowerCase
public String toLowerCase(Locale locale)
Converts all of the characters in thisStringto lower case using the rules of the givenLocale. Case mapping is based on the Unicode Standard version specified by theCharacterclass. Since case mappings are not always 1:1 char mappings, the resultingStringmay be a different length than the originalString.Examples of lowercase mappings are in the following table:
Language Code of Locale Upper Case Lower Case Description tr (Turkish) \u0130 \u0069 capital letter I with dot above -> small letter i tr (Turkish) \u0049 \u0131 capital letter I -> small letter dotless i (all) French Fries french fries lowercased all chars in String (all) 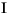
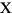
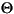
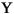
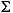
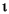
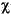
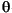
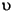
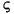
lowercased all chars in String - Parameters:
locale- use the case transformation rules for this locale- Returns:
- the
String, converted to lowercase. - Since:
- 1.1
- See Also:
toLowerCase(),toUpperCase(),toUpperCase(Locale)
-
toLowerCase
public String toLowerCase()
Converts all of the characters in thisStringto lower case using the rules of the default locale. This is equivalent to callingtoLowerCase(Locale.getDefault()).Note: This method is locale sensitive, and may produce unexpected results if used for strings that are intended to be interpreted locale independently. Examples are programming language identifiers, protocol keys, and HTML tags. For instance,
"TITLE".toLowerCase()in a Turkish locale returns"t\u0131tle", where '\u0131' is the LATIN SMALL LETTER DOTLESS I character. To obtain correct results for locale insensitive strings, usetoLowerCase(Locale.ROOT).- Returns:
- the
String, converted to lowercase. - See Also:
toLowerCase(Locale)
-
toUpperCase
public String toUpperCase(Locale locale)
Converts all of the characters in thisStringto upper case using the rules of the givenLocale. Case mapping is based on the Unicode Standard version specified by theCharacterclass. Since case mappings are not always 1:1 char mappings, the resultingStringmay be a different length than the originalString.Examples of locale-sensitive and 1:M case mappings are in the following table.
Language Code of Locale Lower Case Upper Case Description tr (Turkish) \u0069 \u0130 small letter i -> capital letter I with dot above tr (Turkish) \u0131 \u0049 small letter dotless i -> capital letter I (all) \u00df \u0053 \u0053 small letter sharp s -> two letters: SS (all) Fahrvergnügen FAHRVERGNÜGEN - Parameters:
locale- use the case transformation rules for this locale- Returns:
- the
String, converted to uppercase. - Since:
- 1.1
- See Also:
toUpperCase(),toLowerCase(),toLowerCase(Locale)
-
toUpperCase
public String toUpperCase()
Converts all of the characters in thisStringto upper case using the rules of the default locale. This method is equivalent totoUpperCase(Locale.getDefault()).Note: This method is locale sensitive, and may produce unexpected results if used for strings that are intended to be interpreted locale independently. Examples are programming language identifiers, protocol keys, and HTML tags. For instance,
"title".toUpperCase()in a Turkish locale returns"T\u0130TLE", where '\u0130' is the LATIN CAPITAL LETTER I WITH DOT ABOVE character. To obtain correct results for locale insensitive strings, usetoUpperCase(Locale.ROOT).- Returns:
- the
String, converted to uppercase. - See Also:
toUpperCase(Locale)
-
trim
public String trim()
Returns a string whose value is this string, with any leading and trailing whitespace removed.If this
Stringobject represents an empty character sequence, or the first and last characters of character sequence represented by thisStringobject both have codes greater than'\u0020'(the space character), then a reference to thisStringobject is returned.Otherwise, if there is no character with a code greater than
'\u0020'in the string, then aStringobject representing an empty string is returned.Otherwise, let k be the index of the first character in the string whose code is greater than
'\u0020', and let m be the index of the last character in the string whose code is greater than'\u0020'. AStringobject is returned, representing the substring of this string that begins with the character at index k and ends with the character at index m-that is, the result ofthis.substring(k, m + 1).This method may be used to trim whitespace (as defined above) from the beginning and end of a string.
- Returns:
- A string whose value is this string, with any leading and trailing white space removed, or this string if it has no leading or trailing white space.
-
toString
public String toString()
This object (which is already a string!) is itself returned.- Specified by:
toStringin interfaceCharSequence- Overrides:
toStringin classObject- Returns:
- the string itself.
-
chars
public IntStream chars()
Returns a stream ofintzero-extending thecharvalues from this sequence. Any char which maps to a surrogate code point is passed through uninterpreted.- Specified by:
charsin interfaceCharSequence- Returns:
- an IntStream of char values from this sequence
- Since:
- 1.9
-
codePoints
public IntStream codePoints()
Returns a stream of code point values from this sequence. Any surrogate pairs encountered in the sequence are combined as if by Character.toCodePoint and the result is passed to the stream. Any other code units, including ordinary BMP characters, unpaired surrogates, and undefined code units, are zero-extended tointvalues which are then passed to the stream.- Specified by:
codePointsin interfaceCharSequence- Returns:
- an IntStream of Unicode code points from this sequence
- Since:
- 1.9
-
toCharArray
public char[] toCharArray()
Converts this string to a new character array.- Returns:
- a newly allocated character array whose length is the length of this string and whose contents are initialized to contain the character sequence represented by this string.
-
format
public static String format(String format, Object... args)
Returns a formatted string using the specified format string and arguments.The locale always used is the one returned by
Locale.getDefault().- Parameters:
format- A format stringargs- Arguments referenced by the format specifiers in the format string. If there are more arguments than format specifiers, the extra arguments are ignored. The number of arguments is variable and may be zero. The maximum number of arguments is limited by the maximum dimension of a Java array as defined by The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification. The behaviour on anullargument depends on the conversion.- Returns:
- A formatted string
- Throws:
IllegalFormatException- If a format string contains an illegal syntax, a format specifier that is incompatible with the given arguments, insufficient arguments given the format string, or other illegal conditions. For specification of all possible formatting errors, see the Details section of the formatter class specification.- Since:
- 1.5
- See Also:
Formatter
-
format
public static String format(Locale l, String format, Object... args)
Returns a formatted string using the specified locale, format string, and arguments.- Parameters:
l- The locale to apply during formatting. Iflisnullthen no localization is applied.format- A format stringargs- Arguments referenced by the format specifiers in the format string. If there are more arguments than format specifiers, the extra arguments are ignored. The number of arguments is variable and may be zero. The maximum number of arguments is limited by the maximum dimension of a Java array as defined by The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification. The behaviour on anullargument depends on the conversion.- Returns:
- A formatted string
- Throws:
IllegalFormatException- If a format string contains an illegal syntax, a format specifier that is incompatible with the given arguments, insufficient arguments given the format string, or other illegal conditions. For specification of all possible formatting errors, see the Details section of the formatter class specification- Since:
- 1.5
- See Also:
Formatter
-
valueOf
public static String valueOf(Object obj)
Returns the string representation of theObjectargument.- Parameters:
obj- anObject.- Returns:
- if the argument is
null, then a string equal to"null"; otherwise, the value ofobj.toString()is returned. - See Also:
Object.toString()
-
valueOf
public static String valueOf(char[] data)
Returns the string representation of thechararray argument. The contents of the character array are copied; subsequent modification of the character array does not affect the returned string.- Parameters:
data- the character array.- Returns:
- a
Stringthat contains the characters of the character array.
-
valueOf
public static String valueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count)
Returns the string representation of a specific subarray of thechararray argument.The
offsetargument is the index of the first character of the subarray. Thecountargument specifies the length of the subarray. The contents of the subarray are copied; subsequent modification of the character array does not affect the returned string.- Parameters:
data- the character array.offset- initial offset of the subarray.count- length of the subarray.- Returns:
- a
Stringthat contains the characters of the specified subarray of the character array. - Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifoffsetis negative, orcountis negative, oroffset+countis larger thandata.length.
-
copyValueOf
public static String copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count)
Equivalent tovalueOf(char[], int, int).- Parameters:
data- the character array.offset- initial offset of the subarray.count- length of the subarray.- Returns:
- a
Stringthat contains the characters of the specified subarray of the character array. - Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifoffsetis negative, orcountis negative, oroffset+countis larger thandata.length.
-
copyValueOf
public static String copyValueOf(char[] data)
Equivalent tovalueOf(char[]).- Parameters:
data- the character array.- Returns:
- a
Stringthat contains the characters of the character array.
-
valueOf
public static String valueOf(boolean b)
Returns the string representation of thebooleanargument.- Parameters:
b- aboolean.- Returns:
- if the argument is
true, a string equal to"true"is returned; otherwise, a string equal to"false"is returned.
-
valueOf
public static String valueOf(char c)
Returns the string representation of thecharargument.- Parameters:
c- achar.- Returns:
- a string of length
1containing as its single character the argumentc.
-
valueOf
public static String valueOf(int i)
Returns the string representation of theintargument.The representation is exactly the one returned by the
Integer.toStringmethod of one argument.- Parameters:
i- anint.- Returns:
- a string representation of the
intargument. - See Also:
Integer.toString(int, int)
-
valueOf
public static String valueOf(long l)
Returns the string representation of thelongargument.The representation is exactly the one returned by the
Long.toStringmethod of one argument.- Parameters:
l- along.- Returns:
- a string representation of the
longargument. - See Also:
Long.toString(long)
-
valueOf
public static String valueOf(float f)
Returns the string representation of thefloatargument.The representation is exactly the one returned by the
Float.toStringmethod of one argument.- Parameters:
f- afloat.- Returns:
- a string representation of the
floatargument. - See Also:
Float.toString(float)
-
valueOf
public static String valueOf(double d)
Returns the string representation of thedoubleargument.The representation is exactly the one returned by the
Double.toStringmethod of one argument.- Parameters:
d- adouble.- Returns:
- a string representation of the
doubleargument. - See Also:
Double.toString(double)
-
intern
public String intern()
Returns a canonical representation for the string object.A pool of strings, initially empty, is maintained privately by the class
String.When the intern method is invoked, if the pool already contains a string equal to this
Stringobject as determined by theequals(Object)method, then the string from the pool is returned. Otherwise, thisStringobject is added to the pool and a reference to thisStringobject is returned.It follows that for any two strings
sandt,s.intern() == t.intern()istrueif and only ifs.equals(t)istrue.All literal strings and string-valued constant expressions are interned. String literals are defined in section 3.10.5 of the The Java™ Language Specification.
- Returns:
- a string that has the same contents as this string, but is guaranteed to be from a pool of unique strings.
-
-